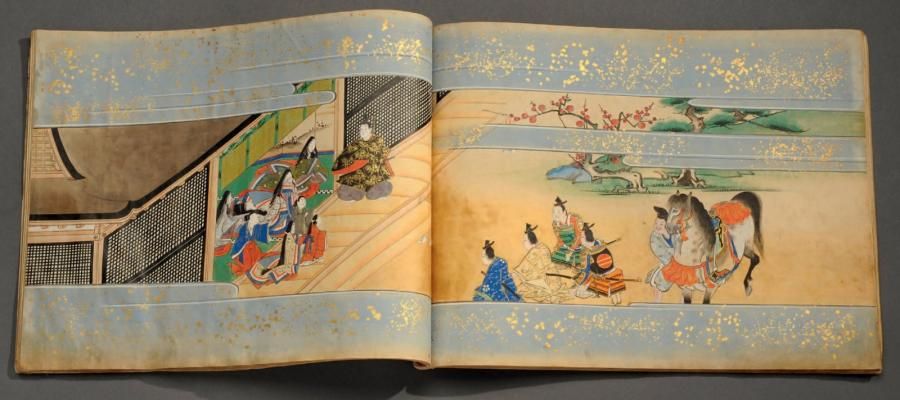
Issu, comme tous les arts de l’Extrême-Orient, de la Chine qui lui a fourni techniques et modèles, l’art japonais se distingue, cependant, par l’originalité de ses créations. Lorsque, aux VIe et VIIe siècles, le Japon s’ouvre aux influences continentales sous le couvert du bouddhisme, il se met avec application à l’école des artisans venus de Corée pour l’initier.
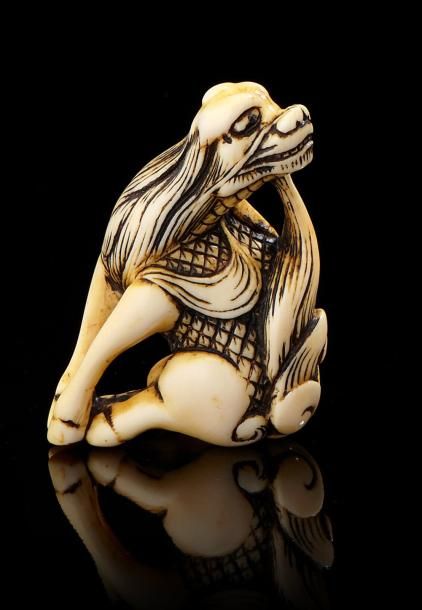
Les premières véritables œuvres d’art japonaises datent du 2ème millénaire avant notre ère lorsque la céramique sort de son rôle strictement utilitaire pour devenir ornementale. À la même époque, les artisans produisent également des masques en coquillages et, plus tard, en argile ainsi que des figurines, les dogū.
À la veille de l’Ère commune, le Japon est envahi par des peuplades venues de Chine et de Corée et adopte une partie de leurs traditions culturelles. Les productions artisanales en seront influencées dans le travail du cuivre et du bronze.
La société japonaise est bouleversée vers le 6ème siècle, lorsque le bouddhisme se répand dans l’archipel. La culture se transforme en parallèle et les influences coréennes et chinoises, mais également indiennes, se retrouvent notamment dans l’architecture, dans la sculpture ou dans l’adoption de la technique de la laque. Les principales œuvres de cette époque se rapportent à la religion, statues de Bouddha, gongs ou brûle-encens







![PEINTRES D'ASIE, ŒUVRES MAJEURES • VENTE [38]](https://cdn.drouot.com/d/image/vente?size=phare&path=78/134916/d155071746784705b81ca19f51f98bd0)